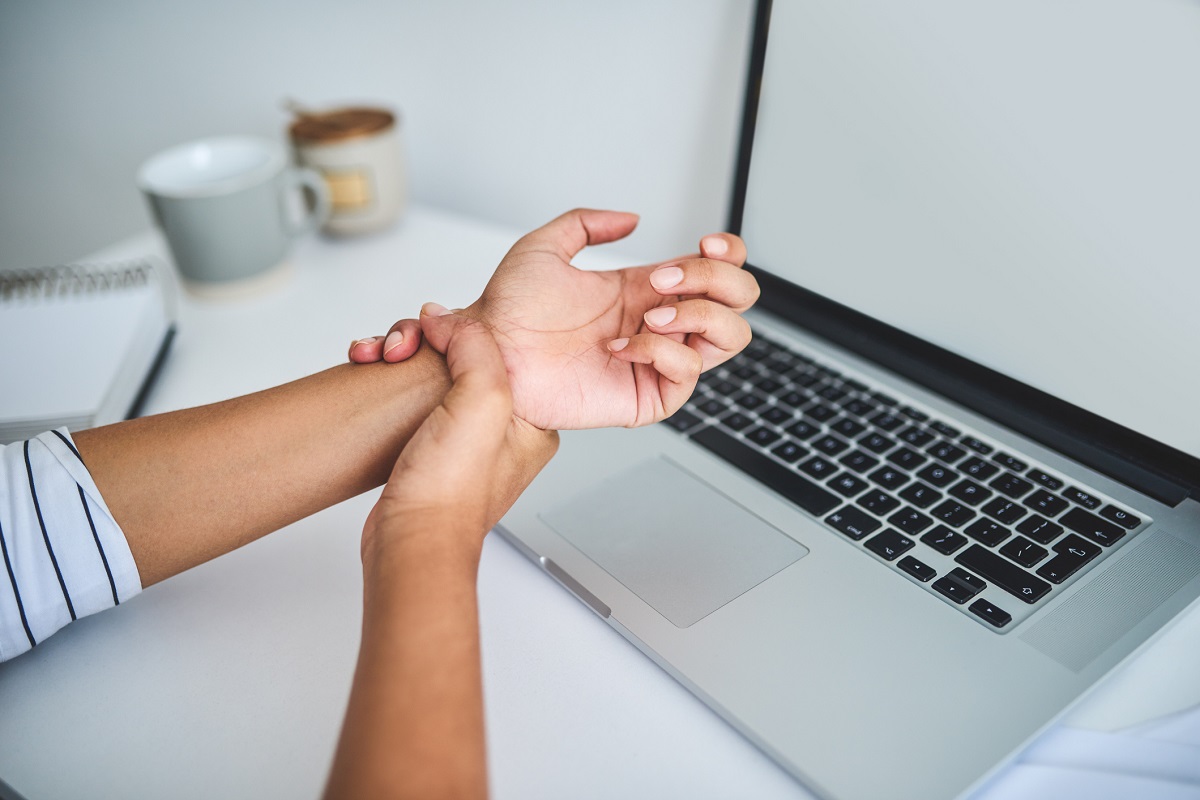


Ultrasound imaging to check for abnormal size of the median nerve.Electrodiagnostic tests, such as nerve conduction studies and electromyography, to determine the severity of damage to the median nerve.In addition to a physical exam, other testing may be done, including: UT Southwestern physicians will also rule out conditions that mimic carpal tunnel syndrome. Diagnosis usually begins with a physical exam of the hands, arms, shoulders, and neck to check for movement dysfunction, atrophy, tenderness, swelling, warmth, and discoloration. When carpal tunnel syndrome is diagnosed early, it is much easier to treat. It’s important to get a diagnosis from a physician to identify the most effective treatment. The symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome can be similar to other medical conditions or problems. Some people with very severe carpal tunnel syndrome have trouble feeling hot and cold by touch and might therefore burn their fingertips without knowing it. In chronic or untreated cases, the muscles at the base of the thumb may waste away. Weakness when gripping objects with one or both hands.Pins-and-needles feeling in the fingers.Pain or numbness that is worse at night, interrupting sleep.Feeling the need to shake out the hand or wrist.Burning or tingling in the fingers, especially the thumb and the first two fingers.Symptoms can include any of the following: The dominant hand tends to have more severe symptoms. Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome usually start gradually, appearing in one or both hands during the night. While numerous studies have explored the association between computer use and carpal tunnel syndrome, there is not yet consistent evidence that clearly links extensive computer use with carpal tunnel syndrome. None of these factors have been established as direct causes of carpal tunnel syndrome. Family history of carpal tunnel syndrome.Other conditions or injuries of the wrist, including strain, sprain, dislocation, break, or swelling and inflammation.Hormonal or metabolic changes, such as menopause, pregnancy, thyroid imbalance, or an overactive pituitary gland.Joint or bone disease, such as arthritis, osteoarthritis, or rheumatoid arthritis.Frequent and repetitive grasping movements with the hands, such as with sports and certain other physical activities.Frequent and repetitive small movements with the hands, such as with typing or using a keyboard.
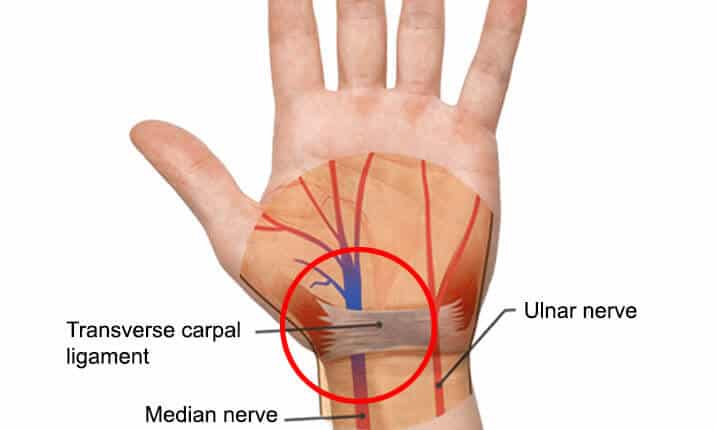
In treating carpal tunnel syndrome, specialists at UT Southwestern perform surgery only if absolutely necessary. If this nerve gets compressed or irritated, symptoms may develop such as numbness, weakness, or sometimes pain in the hand, wrist, and forearm. The median nerve provides sensory and motor functions to the thumb and first three fingers. Expert Care for Optimal Carpal Tunnel Syndrome ResultsĬarpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes pressed or squeezed at the carpal tunnel – a narrow, rigid passageway of ligament and bones at the wrist.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
